Usefulness of the methods
Quantification of drug effects against symptoms of common motion sickness is a useful practical aim which can be realised by the methods offered by HPR. Many drugs which are effective against motion sickness more or less reduce vigilance and performance at least at higher dosages. Concomitant measurement of vigilance and performance allows comparing the anti-motion sickness dose range with that influencing vigilance and performance in order to detect effective doses with tolerable side effects for ambulant treatment.
Principle of the methods
Electro-Nystagmography
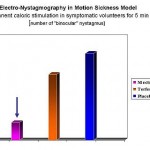 Persisting nystagm is initiated by permanent caloric stimulation of the eardrum (respectively the vestibular apparatus). The resulting nystagm is recorded by surface skin electrodes and evaluated on-line by a sophisticated computer programme (for an example in successful reduction of nystagm by anti-motion-sickness compounds see left fig.).
Persisting nystagm is initiated by permanent caloric stimulation of the eardrum (respectively the vestibular apparatus). The resulting nystagm is recorded by surface skin electrodes and evaluated on-line by a sophisticated computer programme (for an example in successful reduction of nystagm by anti-motion-sickness compounds see left fig.).
Vegetative symptoms
 Caloric stimulation initiates changes in Na-secretion in the sweat, and in vital signs as heart rate and blood pressure. The latter parameters are recorded and evaluated on-line (for an example in successful reduction of Na-secretion by anti-motion-sickness compounds see left fig.).
Caloric stimulation initiates changes in Na-secretion in the sweat, and in vital signs as heart rate and blood pressure. The latter parameters are recorded and evaluated on-line (for an example in successful reduction of Na-secretion by anti-motion-sickness compounds see left fig.).
Measurement of vigilance and performance
Combination with our test battery investigating vigilance and performance provides quantitative information on the most important undesired effect of drugs which are effective against motion sickness.
Advantages of the methods
In contrast to rotatory induction of vestibular symptoms and nystagm, the caloric stimulation in our experimental setting – in connection with nystagmography and vital sign evaluations – in our experimental setting is a longer-lasting and reproducible exposure. This enables not only the quantification of anti-motion sickness effects but also the recording of their onset, maximum and duration.
Reference data
Data are available for several antihistamines with and without caffeine.
Options
- Combination with (sedational) measurement of vigilance and CNS-performance
- Proof of anti-motion-sickness effects of drugs
- Determination of the dose-effect and time-effect relationships of anti-motion sickness drugs
- Concomitant measurement of pharmacokinetics